-
Analyzing Buffer Overflow Vulnerabilities with CodeQL - Claude
-
New dataflow API for writing custom CodeQL queries - GitHub Changelog
Grammar
codeql的代码结构和面向对象语言例如java初看上去有点类似,有class和继承的层级。predict取代了函数。
和普通编程语言不一样的是,函数(predict)体由formula, expression组成,更贴近一种逻辑编程语言而非传统的过程式语言。
例如,这里的exists formula
exists(variable definition | formula)
表示能够找到这样的formula,使得这里出现的free variable有一个bonding。
DataFlow
一个数据流中的Node(有expression node和parameter node之分)表示数据可以流向的结点。asExpr或者asIndirectExpr转化成ast中的一个表达式;asParameter和asIndirectParameter转换成一个pamameter。
class Node {
/**
* Gets the expression corresponding to this node, if any.
*/
Expr asExpr() { ... }
/**
* Gets the expression corresponding to a node that is obtained after dereferencing
* the expression `index` times, if any.
*/
Expr asIndirectExpr(int index) { ... }
/**
* Gets the parameter corresponding to this node, if any.
*/
Parameter asParameter() { ... }
/**
* Gets the parameter corresponding to a node that is obtained after dereferencing
* the parameter `index` times.
*/
Parameter asParameter(int index) { ... }
...
}用户声明一个implemts了DataFlow::ConfigSig或者DataFlow::StateConfigSig的module,实现isSource和isSink方法。
sanitizers and barriers
sanitizers和barriers是用来block掉数据流的传输,用于标记对污点的过滤操作。
数据流向的结点如果在barrier之上那么就会终结数据流的流动。
Taint Tracking
相比data flow而言,taint tracking能够跟踪数据的改变情况(如果发生了改变会继续跟踪)。例如,下面提供一个例子:
#include <stdio.h>
int my_source()
{
return 42;
}
void my_sink(int x)
{
}
int main()
{
int ret = my_source();
my_sink(ret);
my_sink(ret + 1);
}import cpp
import semmle.code.cpp.dataflow.new.TaintTracking
import semmle.code.cpp.dataflow.new.DataFlow
module MySourceToSinkConfig implements DataFlow::ConfigSig {
predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node source) {
exists(FunctionCall fc |
fc.getTarget().getName() = "my_source" and
source.asExpr() = fc
)
}
predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) {
exists(FunctionCall printfCall |
printfCall.getTarget().getName() = "my_sink" and
sink.asExpr() = printfCall.getArgument(0)
)
}
}
module MySourceToSinkFlow = TaintTracking::Global<MySourceToSinkConfig>;
//module MySourceToSinkFlow = DataFlow::Global<MySourceToSinkConfig>;
from DataFlow::Node source, DataFlow::Node sink
where MySourceToSinkFlow::flow(source, sink)
select sink, "Tainted value from my_source() is passed to printf"这里如果使用DataFlow那么只会产生一个查询结果。
Examples
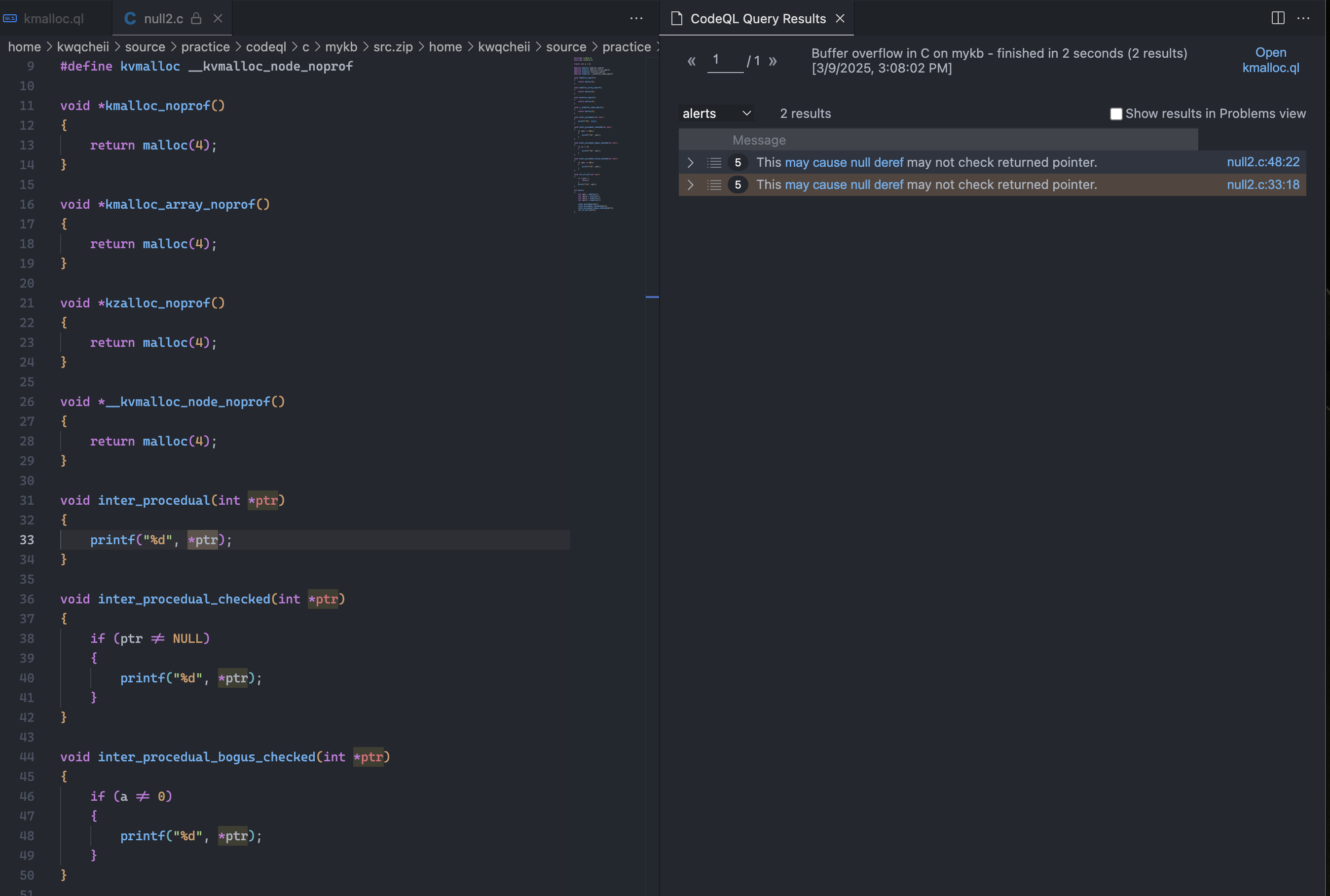
这里给出一个检查null deref的简单小例子。对kmalloc系列函数作为source,对指针解引用作为sink,对检查的条件分支标记为barrier。
import cpp
import semmle.code.cpp.dataflow.new.DataFlow
import semmle.code.cpp.dataflow.new.TaintTracking
import semmle.code.cpp.controlflow.Guards
import NullDerefFlow::PathGraph
module SensitiveLoggerConfig implements DataFlow::ConfigSig {
predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node source) {
exists(FunctionCall fc |
(
fc.getTarget().getName().matches("kmalloc%") or
fc.getTarget().getName().matches("kzalloc%")
) and
source.asExpr() = fc
)
}
predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) {
exists(Expr e |
e = sink.asExpr() and
(
e instanceof PointerDereferenceExpr
or
e instanceof PointerFieldAccess
or
e instanceof ArrayExpr and
e.(ArrayExpr).getArrayBase().getType().stripType() instanceof PointerType
)
)
}
predicate isBarrier(DataFlow::Node node) {
exists(GuardCondition gc | node.asExpr() = gc.getAChild*())
}
}
module NullDerefFlow = TaintTracking::Global<SensitiveLoggerConfig>;
from NullDerefFlow::PathNode source, NullDerefFlow::PathNode sink
where NullDerefFlow::flowPath(source, sink)
select sink.getNode(), source, sink, "This $@ may not check returned pointer.", source.getNode(),
"may cause null deref"
测试c语言示例如下。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
static int a = 0;
#define kmalloc kmalloc_noprof
#define kcalloc kmalloc_array_noprof
#define kzmalloc kzalloc_noprof
#define kvmalloc __kvmalloc_node_noprof
void *kmalloc_noprof()
{
return malloc(4);
}
void *kmalloc_array_noprof()
{
return malloc(4);
}
void *kzalloc_noprof()
{
return malloc(4);
}
void *__kvmalloc_node_noprof()
{
return malloc(4);
}
void inter_procedual(int *ptr)
{
printf("%d", *ptr);
}
void inter_procedual_checked(int *ptr)
{
if (ptr != NULL)
{
printf("%d", *ptr);
}
}
void inter_procedual_bogus_checked(int *ptr)
{
if (a != 0)
{
printf("%d", *ptr);
}
}
void inter_procedual_false_checked(int *ptr)
{
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%d", *ptr);
}
}
void ret_if_null(int *ptr)
{
if (!ptr) {
return;
}
printf("%d", *ptr);
}
int main()
{
int *ptr = kmalloc();
int *ptr2 = kcalloc();
int *ptr3 = kzmalloc();
int *ptr4 = kzmalloc();
inter_procedual(ptr);
inter_procedual_checked(ptr2);
inter_procedual_bogus_checked(ptr3);
ret_if_null(ptr4);
}